Plastic Extrusion Machine Show
JianTai Plastic Extrusion Machine 20 Years of Experience
Among the numerous manufacturers of plastic extrusion machines, Jiantai stands out as a true pioneer, boasting an impressive 20-year legacy of excellence in the industry. This Chinese company has earned a reputation for producing reliable, high-quality extrusion machines that cater to a wide range of applications, from film and sheet extrusion to pipe and profile production.
Jiantai’s journey began in the early 2000s when the company recognized the growing demand for efficient and cost-effective plastic extrusion solutions. With a team of experienced engineers and a commitment to innovation, Jiantai set out to develop extrusion machines that would not only meet but exceed the industry standards.
Over the past two decades, Jiantai has continuously pushed the boundaries of extrusion technology, introducing various models and configurations to address the diverse needs of plastic processors. Their product lineup includes single-screw extruders, twin-screw extruders, and specialized extrusion lines for applications such as PVC, WPC (Wood-Plastic Composites), and more.
Technological Advancements and Innovation
One of the key factors that have contributed to Jiantai’s success is their dedication to technological advancements and innovation. The company invests heavily in research and development, continuously exploring new materials, designs, and processes to enhance the performance and efficiency of their extrusion machines.
Jiantai’s extrusion machines are known for their precise temperature control systems, advanced screw designs, and optimized barrel configurations, which ensure consistent output and high-quality end products. Additionally, the company has integrated Industry 4.0 concepts into their machines, enabling real-time monitoring, data analysis, and remote control capabilities.
Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
In today’s environmentally conscious world, energy efficiency and sustainability have become paramount considerations in the plastic extrusion industry. Jiantai recognized this trend early on and has made significant strides in developing energy-efficient extrusion machines that consume less power while maintaining high production rates.
The company’s patented technologies, such as their Advanced Energy Saving System (AESS), have been instrumental in reducing energy consumption and minimizing the carbon footprint of their extrusion machines. Moreover, Jiantai’s machines are designed to be compatible with a wide range of eco-friendly and recycled plastic materials, further promoting sustainability in the industry.
Global Footprint and Customer Support
Jiantai’s success is not limited to its home country of China. Over the years, the company has expanded its global footprint, establishing a strong presence in various international markets, including Europe, North America, and Southeast Asia. This global reach has allowed Jiantai to cater to the diverse needs of customers worldwide and adapt to regional preferences and regulations.
Furthermore, Jiantai places a strong emphasis on customer support and after-sales service. The company offers comprehensive training programs, technical assistance, and a robust spare parts supply chain to ensure that their customers can maximize the productivity and longevity of their extrusion machines.
Looking Ahead
As Jiantai celebrates 20 years of excellence in the plastic extrusion industry, the company shows no signs of slowing down. With a continued focus on innovation, sustainability, and customer satisfaction, Jiantai is well-positioned to maintain its leadership position and contribute to the advancement of plastic extrusion technology.
The company’s commitment to staying ahead of industry trends, investing in research and development, and embracing digitalization and automation will undoubtedly shape the future of plastic extrusion machines. As the global demand for high-quality, efficient, and eco-friendly extrusion solutions continues to grow, Jiantai’s expertise and experience will be invaluable assets for plastic processors worldwide.
Recommended Products Plastic Recycling Machine
Making a plastic recycling machine involves steps such as design, procurement, mechanical fabrication, installation of electrical systems, installation of heating systems, and installation of cooling systems. Machine specifications need to be designed, components need to be procured, mechanical parts need to be manufactured and electrical, heating and cooling systems need to be installed.
Plastic Extrusion Machine Video Show
Advanced Plastic Recycling Machinery
High Throughput Plastic Pellet Recycling Machine
Excellent High Output Plastic Recycling Machine
Get in touch with us
Plastic Extrusion Machine Performance Improvement Recommendations
- Optimize Material Selection: Use high-quality plastic raw materials to ensure consistency and suitability, reducing impurities and defective rates during production. Additionally, choose the appropriate plastic type and formulation to meet the requirements of the final product and optimize the efficiency of the extrusion machine.
- Mechanical Maintenance: Regularly maintain the extrusion machine by cleaning, lubricating, and replacing worn parts. Ensure all mechanical components are in optimal condition to minimize failures and downtime, thus improving production efficiency.
- Temperature Control Optimization: Precisely control the heating and cooling systems of the extrusion machine to maintain the proper temperature of the plastic during the extrusion process. Optimizing temperature control can enhance product quality, reduce defect rates, and increase the production capacity of the extrusion machine.
- Adjust Extrusion Machine Parameters: Adjust the parameters of the extrusion machine, including extrusion speed, pressure, and die design, according to the type and specifications of the plastic products being produced. Optimizing these parameters can improve the performance of the extrusion machine and ensure the production of compliant products.
- Automation and Intelligence Improvement: Introduce automation and intelligence technologies such as automated control systems, machine learning algorithms, and remote monitoring systems to enhance the stability and controllability of the production process, reduce human errors, and increase production efficiency.
- Waste Management and Recycling: Develop effective waste management and recycling systems to minimize waste generation and reuse waste in the production process, reducing production costs and environmental impact.
- Training and Skill Enhancement: Provide training for extrusion machine operators to improve their skill levels and operational experience, enabling them to better master operating techniques and adjustment methods for the extrusion machine, thereby increasing production efficiency and product quality.
Questions about Plastic Extrusion Machines
Curious about Plastic Extrusion Machines? Stay tuned as we delve into the world of these vital manufacturing tools. From shaping raw plastic materials to creating pipes and sheets, we’ll explore key components like the extruder and die. Plus, we’ll answer common questions about their operation and performance factors. Get ready to uncover the secrets behind Plastic Extrusion Machines!
Answer: A plastic extrusion machine is a manufacturing device used to shape raw plastic materials into continuous profiles with a specific cross-sectional shape. It works by melting plastic pellets or granules and then forcing the molten material through a die to form the desired shape.
- Answer: Plastic extrusion machines are used in a wide range of industries for various applications, including:
- Manufacturing of pipes and tubing for plumbing, irrigation, and construction.
- Production of profiles for window frames, door frames, and other building materials.
- Fabrication of sheets and films for packaging, signage, and industrial purposes.
- Creation of filaments for 3D printing and additive manufacturing.
- Extrusion of cables and wires for electrical and telecommunications industries.
- Answer: The main components of a plastic extrusion machine include:
- Extruder: A screw mechanism that melts and conveys the plastic material.
- Hopper: A container for holding and feeding raw plastic materials into the extruder.
- Heater: Heating elements that melt the plastic pellets or granules within the extruder.
- Die: A specialized tool that shapes the molten plastic into the desired cross-sectional profile.
- Cooling System: Devices such as air or water cooling systems to solidify the extruded plastic.
- Take-off Equipment: Mechanisms for pulling or cutting the extruded product to the desired length.
- Control Panel: Interface for monitoring and adjusting parameters such as temperature, speed, and pressure.
- Answer: Several factors can influence the performance of a plastic extrusion machine, including:
- Material Quality: The quality and consistency of the raw plastic materials used.
- Temperature Control: Proper heating and cooling to maintain the desired temperature throughout the process.
- Die Design: The design and condition of the die affect the shape and quality of the extruded product.
- Extrusion Speed: The rate at which the plastic material is forced through the die.
- Pressure Control: Controlling the pressure within the extruder to ensure uniform extrusion.
- Maintenance: Regular maintenance and cleaning to prevent equipment failures and downtime.
- Operator Skill: The expertise and experience of the machine operators in operating and troubleshooting the equipment.
Comprehensive Guide to Plastic Extrusion Machine
Plastic extrusion is a widely used process in manufacturing where raw thermoplastic material is melted and formed into a continuous profile. Extrusion produces items like pipe, tubing, weather stripping, fencing, deck railings, window frames, plastic films and sheets. At the heart of the extrusion process is the extrusion machine itself. Understanding how these machines work is essential for anyone involved in plastics manufacturing.
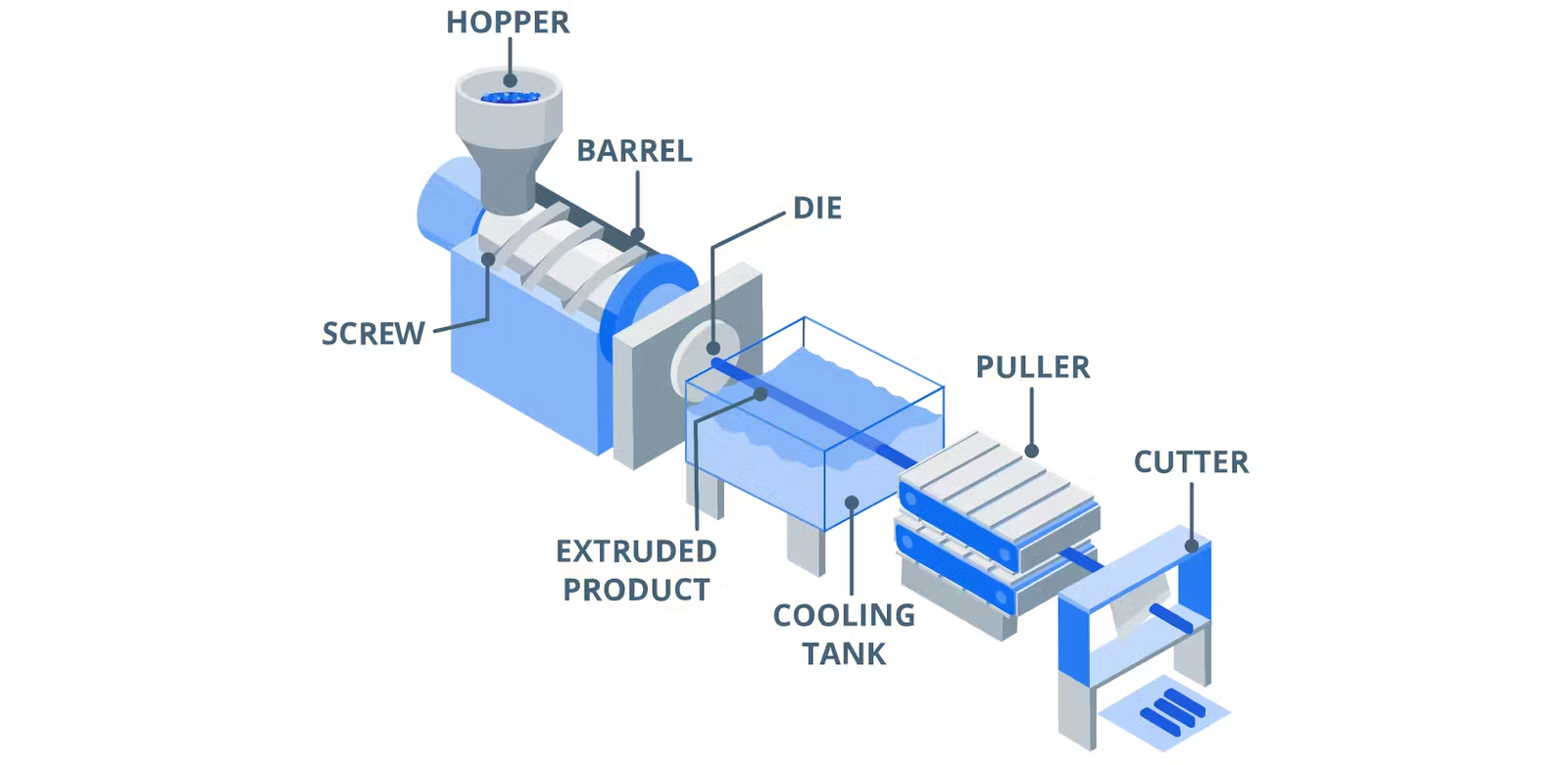
Basic Extrusion Machine Design
A basic single-screw extruder consists of several key components:
- Feeder Hopper – This is where plastic pellets or powder are introduced into the extrusion system. The hopper funnels the material down towards the screw.
- Barrel – This is a heated circular metal cylinder with a spiral groove machined into the interior surface. The rotating screw fits tightly inside this groove.
- Screw – The rotating screw is at the core of the extruder. It serves to compact the plastic, melt it through shear heating and viscous heating from the hot barrel, and pump the molten plastic forward through the die.
- Breaker Plate – This is a metal plate at the end of the barrel with multiple holes drilled through it. It helps build up pressure and ensures even flow of melted plastic before the die.
- Die – The die is the metal plate with a shaped opening through which the molten plastic emerges to form the final extruded product shape.
Other components include heater bands that wrap around the barrel, motors that turn the screw, cooling fans, temperature controllers, and a screen pack filter to trap contaminants.
Extrusion Process
The extrusion process follows this basic sequence:
- Plastic pellets are fed into the hopper and gravity pulls them down towards the rotating screw.
- The screw’s rotating motion forces the pellets through the heated barrel where they are gradually melted by a combination of shear forces, conduction from the hot barrel surface, and heat generated from the mechanical energy of the rotating screw.
- As the molten plastic moves forward along the screw’s helical flights, it gets thoroughly mixed and any remaining pellets get melted.
- The screw’s pumping action generates extremely high pressure that forces the homogenized molten plastic through the breaker plate and die openings.
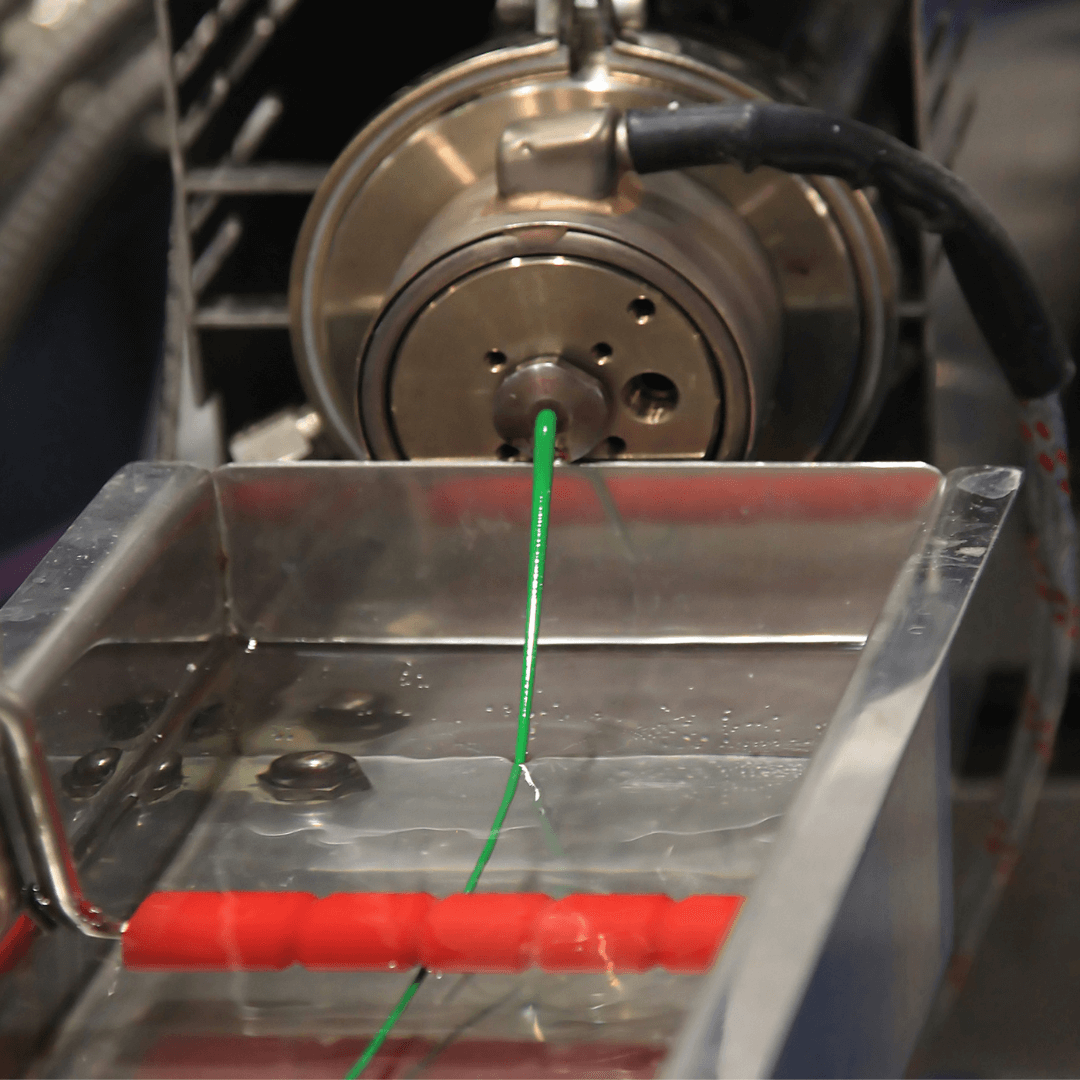
- The extruded polymer leaving the die takes the shape conforming to the die geometry. It then enters a cooling system like a water bath or air wipe to solidify its final shape.
- Downstream equipment like pullers, sizers, cutters, and winders may be used for further size control and processing of the extruded product.
Key Extrusion Variables
The extruder operator controls several key process variables:
- Screw Speed – Increasing the screw’s rotation rpm increases the polymer’s shear heating and extrusion output rate.
- Barrel Temperature Settings – Different zones along the barrel length have individual heater band temperature settings that must be properly controlled based on the polymer’s melt characteristics.
- Die Temperature – The die has separate heating elements to help control the polymer’s viscosity and prevent premature solidification as it exits.
- Back Pressure – The resistance encountered by the polymer melt before it exits the die. This is controlled by adjusting the die intake opening and impacts product quality.
Maintaining the ideal balance of these inter-related variables is crucial for stable and consistent extruded product dimensions, properties, and production rates. Improper settings can lead to problematic defects.
Extruder Types
While all extruders share basic working principles, they are available in various design configurations for specific applications:
Single Screw Extruders
- Most basic and widely used type for commodity polymers like polyethylene, polypropylene, PVC
- Screw has a simple helical groove along its length
Twin Screw Extruders
- Utilize two parallel screws rotating in the same direction (co-rotating) or opposites (counter-rotating)
- Provide intense shear and dispersive mixing, used for reactive extrusion, compounding, devolatilization, dough making
Vented Extruders
- Have venting ports along the barrel to allow removal of volatiles and moisture during extrusion
Grooved Feed Extruders
- Grooved sections on the feed zone of the screw improve intake of difficult to feed materials like heat sensitive polymers
Ram Extruders
- Use a reciprocating ram or piston to pump the polymer melt through the die rather than a turning screw
- Well-suited for applications involving very high extrusion pressures
The screw itself can also vary in design from smooth-bored to barrier, finned, grooved, or other geometries to optimize performance for the specific polymer type.
Extrusion Applications
Due to its versatility and high production rates, extrusion is used to produce a staggering array of plastic products across many industries:
- Pipes and Tubing: Water pipes, electrical conduit, automotive fuel lines
- Window/Door Profiles: Window frames, insulation strips for doors/windows
- Film and Sheet: Packaging films, geomembranes, plastic sheeting
- Wire and Cable: Insulation coatings on wires and fiber optic cables
- Adhesives and Sealants: Butyl rubber sealants, hot melt adhesives
- Medical: Tubing, catheters, IVs
- 3D Printing Filaments: Feed material for fused deposition modeling 3D printers
Other products include weather-stripping, paneling, decking, fencing, and innumerable custom profile extrusions. Extruders are truly the workhorses of the plastics industry.
Safety Considerations
Operating an extrusion line does present some inherent safety hazards that personnel must be aware of:
- Burn Hazards – The extruder barrel and die system operate at extremely high temperatures and can cause severe burns. Proper protective equipment is required.
- Pinch Points – The rotating screw presents pinch point dangers that require safety guards and lockout procedures.
- Material Handling – Dealing with plastic pellets can result in slips/falls. Powders may be combustible as well.
- High Pressure – The extreme pressure involved with extrusion can cause parts failure and instantaneous release of molten polymer if not properly maintained.
- Purging Procedures – Safe purging when switching between polymer types is critical to prevent safety issues and product contamination.
Providing comprehensive safety training, establishing safe operating procedures, using proper PPE, and maintaining equipment in optimal condition are essential for safe, incident-free extrusion operations.
In summary, extrusion is one of the most important and widely utilized processes in the plastics industry. Understanding the fundamentals of how extruders are designed, how the process works, the key variables involved, the range of equipment configurations available, and necessary safety considerations is vital knowledge for anyone in manufacturing. With this comprehensive guide, you are now well-equipped to operate and optimize these impressive workhorses of polymer processing.